In today’s increasingly digital world, the demand for engineers continues to rise. Salary levels are changing yearly, with Japanese engineers earning an average annual income of 5.42 million yen, significantly higher than the all-industry average.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of engineer salaries, concrete methods for increasing income, and future prospects in the field.
- Japanese IT engineers earn ¥5.42M annually, well above national average.
- Experience level can double salary from entry to senior positions.
- AI, cloud, and security specialists will see highest salary growth.
1. The Reality of Engineer Salaries in Japan
Engineer salaries are one of the most discussed topics in Japan’s labor market. With the acceleration of digital transformation (DX), engineer demand increases yearly, and salary levels are changing accordingly.
Average Annual Income of Engineers: 5.42 Million Yen
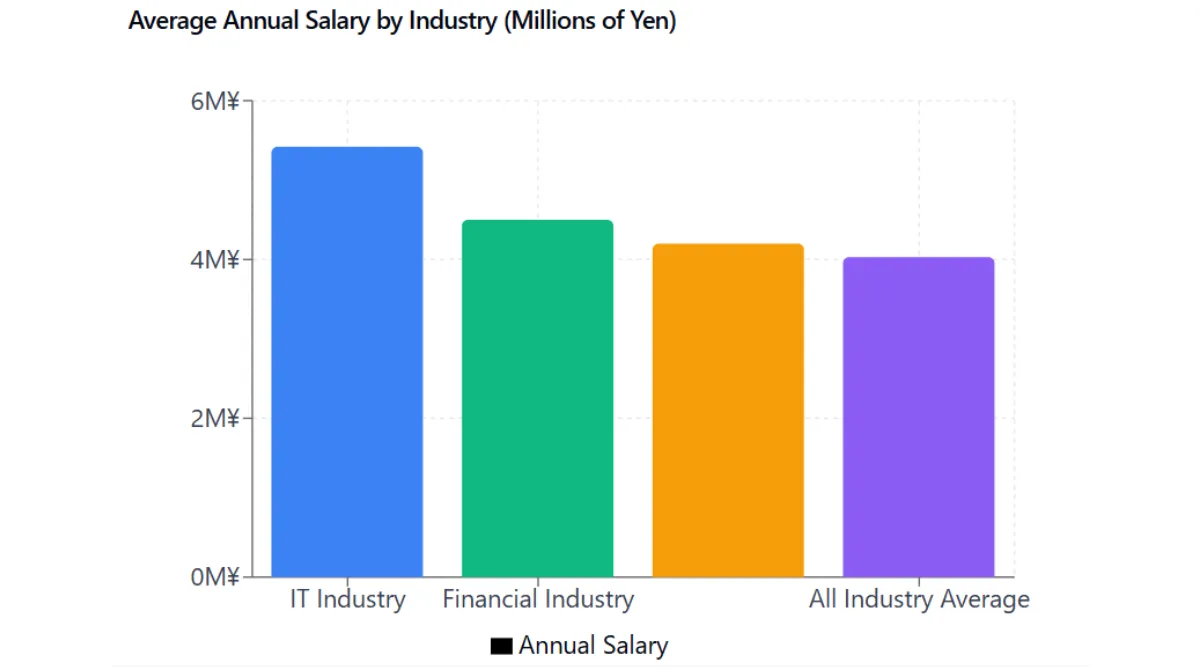
According to the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s “Survey on Salaries in IT-Related Industries,” the average annual income for IT engineers in Japan is 5.42 million yen. This figure is approximately 1.4 million yen higher than the all-industry average of 4.03 million yen.
Looking at different sectors, engineers in the IT industry earn 5.42 million yen, manufacturing industry 4.2 million yen, and financial industry 4.5 million yen, highlighting the notably higher salary levels in the IT sector.
This elevated compensation reflects the increasing demand for digital transformation expertise, the value placed on specialized skills and knowledge, and the necessity of securing talent in a global competitive environment.
Industry Comparison and Position-Specific Salary Ranges
The salary levels vary significantly across different engineering positions.
| Position | Key Responsibilities | Average Annual Income |
|---|---|---|
| Network Engineer | -Infrastructure design -construction -security measures | ¥6.47M |
| IT Consultant | -System strategy planning -project management | ¥6.29M |
| System Engineer | -Wide range of tasks from requirements definition to system design and development | ¥5.32M |
| Web Engineer | -Frontend and backend development | ¥4.80M |
Age and Experience-Based Salary Progression
Engineer salaries vary significantly based on age and years of experience.
- 20s…This period is primarily focused on acquiring fundamental skills, with an average annual income of ¥3.72M.
- 30s…As engineers establish their expertise and gain experience as project leaders, the average annual income rises to ¥5.11M.
- 40s…With enhanced management skills and advanced technical capabilities, the average annual income reaches ¥6.15M.
- 50s and above…Taking on roles in organizational technical strategy planning and mentoring younger engineers, the average annual income reaches ¥6.91M.
Experience-based progression shows similar growth, with salaries ranging from 3.5-4 million yen for those with less than three years of experience, increasing to 4-5 million yen for those with 3-5 years, 5-6 million yen for 5-10 years, and over 6 million yen for professionals with more than a decade in the field.
■Related Reading
The following article provides a detailed explanation of software engineer salaries in Japan, including average annual income and market trends.
2. Three Key Factors Affecting Salaries

1:Skill Level and Salary Correlation
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s IT Skill Standards (ITSS) provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the relationship between skills and compensation.
Entry-level engineers at Level 1 typically earn around 4.37 million yen annually while working on basic development tasks under senior guidance.
Mid-level professionals at Level 3 command 5.82 million yen as they take on independent development work and project management responsibilities.
Senior engineers at Level 5 see their earnings increase to 8.25 million yen as they handle team management and architecture design. Top experts at Level 7, who develop technical strategies and demonstrate global-level achievements, can achieve annual incomes of 11.29 million yen or more.
2:Geographic Location Impact
Location plays a crucial role in determining engineer salaries in Japan. Using Tokyo as a baseline index of 100, salaries in Osaka and Nagoya typically range from 85-90 on this scale. Other major cities fall between 80-85, while regional cities generally range from 70-80. These differences reflect variations in living costs and the concentration of IT companies across regions.
3:Company Size Correlation
The size of the company significantly influences both base salary and overall compensation packages.
Large companies typically offer annual incomes between 6-8 million yen, complemented by multiple annual bonuses and comprehensive benefits.
Mid-sized companies provide more moderate packages, with annual incomes ranging from 4.5-6 million yen and standard benefit structures.
Startups present a more variable environment, with annual incomes between 4-7 million yen, often supplemented by equity options and flexible benefits.
These variations stem from differences in company capital, project scale, investment in talent development, and the maturity of evaluation systems.
Effective skill enhancement requires a systematic learning plan combined with practical project experience. Obtaining technical certifications, participating in technology conferences, and contributing to open-source projects can also significantly increase market value.
3. Strategies for Increasing Engineer Salaries

Achieving higher income as an engineer requires a strategic approach to career development. The most reliable method for increasing compensation is enhancing market value through both technical and business skill development.
In the technical realm, proficiency in cloud technologies (AWS, Azure, GCP), AI and machine learning (TensorFlow, PyTorch), and blockchain development are particularly valuable.
On the business side, project management capabilities, requirements definition and design skills, and technical consulting abilities are increasingly important.
Career Change Considerations
While changing jobs can be an effective means of increasing income, success requires a strategic approach. This includes thorough market research, including industry salary trends, company growth potential, and job market conditions, as well as careful self-analysis of skills, quantifiable achievements, and portfolio development.
The expected salary increase from job changes varies by age group. Professionals in their 20s might see increases of 20-30%, while those in their 30s typically achieve 15-25% increases. The percentage tends to decrease with age, with professionals in their 40s seeing 10-20% increases and those in their 50s typically achieving 5-15% increases.
Effective Salary Negotiation
Salary negotiation represents a crucial opportunity to ensure appropriate recognition of market value. Success in negotiations requires thorough preparation, including market research, quantification of contributions, and organization of specific achievements. During negotiations, it’s essential to present clear evidence of skills, certifications, and numerical results while choosing appropriate timing such as performance reviews or after successful projects.
4. Foreign Engineer Salary Conditions in Japan

Treatment in Japanese Companies
Foreign engineers in Japanese companies typically receive compensation packages that reflect both their technical expertise and unique contributions. The basic salary structure usually mirrors that of Japanese engineers, with additional considerations for language abilities and global project handling.
Benefits often include housing allowances, home leave systems, and Japanese language learning support. This comprehensive approach to compensation recognizes the distinct challenges and contributions of foreign professionals in the Japanese workplace.
Salary Ranges and Progression
The salary structure for foreign engineers typically begins at 3-4 million yen for new graduates, increasing to 4-6 million yen for those with 3-5 years of experience. Engineers with more than five years of experience can expect 5-8 million yen, while senior positions command 8 million yen or more. These figures vary based on technical expertise, Japanese language proficiency, and project responsibility levels.
| Experience Level | Salary Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| New Graduate | ¥3-4M | • Technical skills |
| 3-5 Years | ¥4-6M | • Japanese language proficiency |
| 5+ Years | ¥5-8M | • Project responsibility level |
| Senior Positions | ¥8M+ | • Leadership experience |
Visa Requirements and Compensation
Visa regulations play a significant role in foreign engineer compensation. The Engineer/Specialist in Humanities visa requires a minimum annual income of 3 million yen, with variations based on educational background and work experience.
The Highly Skilled Professional visa employs a point-based system, with additional points awarded for annual incomes exceeding 4 million yen and higher points for those earning over 7 million yen.
■日本でエンジニアとしてキャリアアップしたい方へ
海外エンジニア転職支援サービス『 Bloomtech Career 』にご相談ください。「英語OK」「ビザサポートあり」「高年収企業」など、外国人エンジニア向けの求人を多数掲載。専任のキャリアアドバイザーが、あなたのスキル・希望に合った最適な日本企業をご紹介します。
▼簡単・無料!30秒で登録完了!まずはお気軽にご連絡ください!
Bloomtech Careerに無料相談してみる
5. Future Salary Trends and Prospects

Industry Evolution and Compensation Trends
The IT industry’s salary landscape continues to evolve, driven by ongoing digital transformation initiatives and market expansion. Overall annual salary increases are projected at 3-5% over the next five years, with high-skill professionals potentially seeing 5-10% increases and emerging technology specialists experiencing 10-15% growth.
High-Demand Specializations
Let’s examine the specialized fields expected to see increasing demand.
AI & Machine Learning Engineer
Current annual salary: ¥6-9M
Projected in 5 years: ¥7-12M
*Key skills: Python, TensorFlow, Statistics
Cloud Architect
Current annual salary: ¥7-10M
Projected in 5 years: ¥8-13M
*Key skills: AWS, Azure, Microservices
Security Engineer
Current annual salary: ¥5.5-8.5M
Projected in 5 years: ¥6.5-11M
*Key skills: Information security, Cryptography, Risk management
Career Path Development
Long-term career development in engineering typically follows one of three paths.
The specialist path, focusing on technical expertise and architectural roles, offers potential earnings of 6-15 million yen.
The management path, emphasizing project and organizational leadership, typically provides 7-12 million yen.
A hybrid path combining technical and management responsibilities can command 8-15 million yen.
| Strategic career building requires three key elements: monitoring technical trends and industry developments for market insight, investing in growth areas and continuous skill enhancement, and building professional networks through communities and mentors. This strategic approach to career development maximizes future earning potential. |
6. Conclusion
The engineering profession in Japan continues to see strong salary growth, driven by various factors including skill level, experience, specialization, and company size. As digital transformation accelerates, the demand for engineering talent is expected to increase further, maintaining upward pressure on compensation levels.
Success in maximizing earning potential requires strategic skill development and careful career planning. Engineers who maintain awareness of market trends, invest in high-demand skills, and build strong professional networks position themselves well for ongoing salary growth in this dynamic field.