This article explains the reality of infrastructure engineer salaries and specific methods to increase your income.
If you’re looking for information about infrastructure engineer compensation, you’re not alone.
In fact, infrastructure engineers maintain higher salary levels compared to the average across all professions in Japan, and depending on your career path, an annual income of 10 million yen is well within reach.
- Current salary ranges for infrastructure engineers in Japan
- How to increase your income through certifications and skills
- Top career paths that lead to higher compensation
1.What is an Infrastructure Engineer?

An infrastructure engineer is a technical professional responsible for designing, building, operating, and maintaining an organization’s IT infrastructure (core systems).
They play a crucial role in supporting the fundamental components of systems, including servers, networks, and databases.
In modern business, IT infrastructure has become as essential as water and electricity, and the importance of infrastructure engineers who support it continues to grow year by year.
Types of Infrastructure Engineers
Infrastructure engineering roles can be broadly categorized into three main areas: system infrastructure, network infrastructure, and operations/maintenance.
System Infrastructure
Server engineers and cloud engineers are the most representative roles. Server engineers handle a wide range of responsibilities from physical server design and construction to virtualization environment setup and operation, while cloud engineers build and optimize environments on platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Network Infrastructure
This includes network engineers and security engineers. Network engineers design and build corporate networks and configure routers and switches, while security engineers develop security policies and handle vulnerability countermeasures.
Operations and Maintenance
Operations engineers handle system monitoring and incident response, while maintenance engineers are responsible for regular maintenance and system updates.
Multiple Role Responsibilities
Roles aren’t always clearly divided by organization, and it’s common to handle multiple responsibilities.
As you gain experience, you can advance to positions such as infrastructure architect (designing entire systems and developing technical strategies), team management, or project manager handling project progress management.
To grow as an infrastructure engineer, it’s important to have deep knowledge in specific specialized areas while maintaining broad expertise across related technical fields.
2.Infrastructure Engineer Salary Ranges in Japan
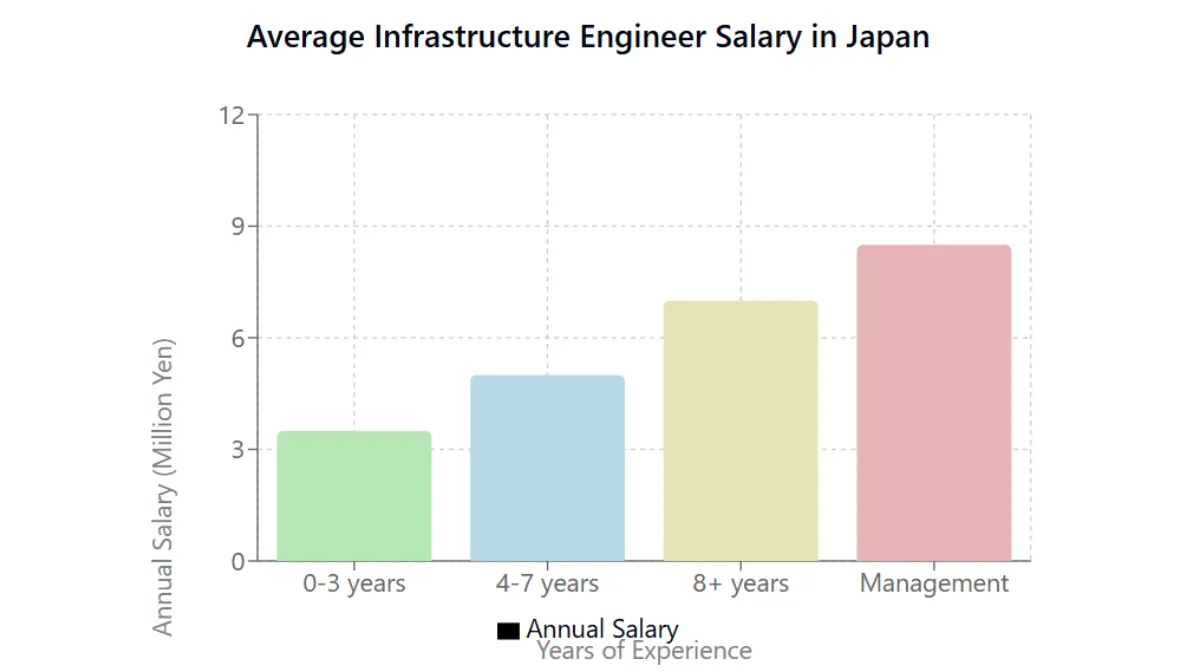
Infrastructure engineer salary levels in Japan maintain higher standards compared to general occupations.
According to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare survey, the average annual income for infrastructure engineers is 6.849 million yen, significantly higher than the national average across all occupations (4.58 million yen).
Average Annual Income by Years of Experience
Infrastructure engineer salaries vary significantly based on years of experience.
For the first three years after graduation, annual income typically ranges from 3-4 million yen, with a basic monthly salary of 200,000-250,000 yen and bonuses equivalent to 3-4 months of basic salary.
Mid-career engineers with 4-7 years of experience see annual incomes rise to 4-6 million yen, with basic monthly salaries increasing to 250,000-350,000 yen.
Veteran engineers (8+ years) typically earn 6-8 million yen annually, with basic monthly salaries of 350,000-450,000 yen and bonuses equivalent to 4-6 months of basic salary.
Furthermore, for those in management or specialist positions, annual incomes exceeding 8 million yen are not uncommon, typically consisting of a basic monthly salary over 450,000 yen plus performance-based bonuses.
Salary Comparison Between Large Companies and Startups
Compensation structures vary significantly based on company size and type.
Salary levels also fluctuate by region, with major metropolitan areas like Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya typically offering 20-30% higher compensation than regional areas. Location and company size are closely related, with both large companies and startups concentrated in metropolitan areas.
Large Companies
Feature stable salary structures with strong emphasis on seniority-based progression and established promotion systems.
Benefits are comprehensive, including social insurance, housing allowances, and family allowances. Bonuses are typically paid twice yearly on a fixed schedule, with relatively small performance-based components.
Startups
Tend to be more merit-based, with potential for larger salary increases.
Basic salaries are often performance-linked, with benefits focusing on flexible work arrangements and stock option programs. Bonuses are predominantly performance-based, with a higher ratio of achievement-based compensation.
Industry-Specific Benefits Worth Noting
The IT industry features unique benefits such as qualification allowances, specialist skill allowances, and project allowances as technical compensation.
Many companies also offer career advancement support through qualification acquisition support programs, technical training programs, and self-development assistance.
3.Factors Affecting Infrastructure Engineer Salaries

Infrastructure engineer salaries vary significantly based on multiple factors.
When aiming for career advancement, it’s important to understand these factors and strategically plan your skill development.
Impact of Certifications on Annual Income
Industry certifications directly influence salary increases.
The value of cloud-related certifications, in particular, continues to rise yearly. Obtaining AWS Solutions Architect certification can lead to salary increases of 500,000 to 1 million yen, which is not uncommon.
Similarly, acquiring Azure Solutions Architect Expert or Google Cloud Professional certifications can potentially increase annual income by 400,000 to 800,000 yen.
In networking, Cisco certifications like CCNP and CCIE are highly valued, with potential salary increases of 300,000 to 600,000 yen upon acquisition.
In the security field, obtaining CCSP certification can lead to income increases of 400,000 to 700,000 yen. Project management certifications like PMP and ITIL Expert can each contribute to salary increases of 200,000 to 500,000 yen.
Income Increases Through Specialization
Deep knowledge and experience in specific specialized fields significantly enhance market value. Developing expertise can lead to substantial increases above standard salary levels.
The security field particularly values specialists in vulnerability assessment, incident response, and security architecture.
In cloud computing, skills in multi-cloud environment design, cloud-native development, and migration expertise are highly sought after. The automation and DevOps fields also show high demand for expertise in CI/CD environment setup, Infrastructure as Code, and container technologies.
Geographic Salary Differences
Location continues to significantly impact salary levels.
Tokyo salaries are typically 20-30% higher than regional areas, often with additional urban allowances of 20,000-50,000 yen monthly. Project rates are also generally higher in Tokyo.
Other major metropolitan areas like Osaka and Nagoya offer salaries 10-15% lower than Tokyo, but usually include urban allowances of 10,000-30,000 yen monthly.
Regional cities typically offer base salaries 20-30% lower than Tokyo, but living costs are also 20-30% lower.
With the recent rise in remote work, opportunities to work on urban projects while living in regional areas have increased, gradually reducing salary disparities.
However, many projects still require on-site work, and complete salary standardization is expected to take more time.
4.Career Paths to High-Income Positions

Infrastructure engineers have multiple career path options, each offering potential for annual incomes exceeding 10 million yen.
Let’s explore the most promising career paths in terms of compensation.
Advancing to Cloud Architect
Cloud architects are among the most in-demand and well-compensated positions in modern IT infrastructure.
This role requires capabilities in multi-cloud environment design and construction, cost optimization strategy development, and security architecture design.
Particularly Important Practical Experience
- Cloud migration project experience
- Large-scale system design experience
- Experience with multiple cloud services
While this field requires continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies due to rapid evolution, market value is correspondingly high.
Path as a Security Specialist
The security field consistently faces talent shortages, offering high compensation for advanced expertise. As a security architect, responsibilities include establishing security policies, company-wide security design, and risk assessment.
Alternatively, you can specialize as a penetration tester, focusing on vulnerability assessment, security audits, and incident response. With cybersecurity growing increasingly important each year, careers in this field can expect stable income prospects.
Transition to Management Positions
By developing management skills in addition to technical expertise, you can aim for higher compensation.
Career Step Examples
- Team leader roles involving small team supervision, technical guidance, and project management
- Project manager positions handling large-scale project oversight, budget management, and client negotiations
- IT department manager roles including department strategy planning, talent development, and vendor management
Compensation includes base salary increases plus position and management allowances.
Additional benefits may include performance-based bonuses, stock options, and performance-linked incentives. Executive promotion possibilities also exist, offering potential for higher income.
Combining Technical Expertise with Management Skills
Career paths aren’t mutually exclusive; combining technical expertise with management skills can open up further income growth opportunities.
Regardless of the chosen path, continuous learning and practical application are essential.
■日本でエンジニアとしてキャリアアップしたい方へ
海外エンジニア転職支援サービス『 Bloomtech Career 』にご相談ください。「英語OK」「ビザサポートあり」「高年収企業」など、外国人エンジニア向けの求人を多数掲載。専任のキャリアアドバイザーが、あなたのスキル・希望に合った最適な日本企業をご紹介します。
▼簡単・無料!30秒で登録完了!まずはお気軽にご連絡ください!
Bloomtech Careerに無料相談してみる
5.Practical Methods for Japanese Infrastructure Engineers to Increase Salary

To practically achieve salary increases as an infrastructure engineer, a planned approach is necessary. Below, we’ll detail proven specific methods.
Real Examples of Income Increase Through Job Changes
Strategic job changes are known as an effective means of salary increase.
Examples of moving to large companies: Often results in 1-2 million yen income increases, plus improved stability and enhanced benefits.
Examples of moving to startups: Potential for 1.5-3 million yen income increases, with possible stock options and increased autonomy.
Keys to Successful Job Changes
Understanding market value is crucial for successful job changes.
Pre-change preparation should include researching industry salary levels, skills inventory, and job market trend analysis to negotiate more favorable terms.
During negotiations, aim for a 30% increase from current annual income as a guideline, based on your skills. It’s also important to confirm future career path opportunities.
Achieving Income Increases Through Skill Development
Planned skill development leads to reliable income increases.
Particularly effective are cloud certifications, security-related certifications, and project management certifications.
Experience in large-scale projects, new technology implementation projects, and client negotiations are also valued as important practical experience.
Specific Income Increase Examples
Year 1: 200,000-300,000 yen increase through basic certification acquisition Year 2: 300,000-500,000 yen increase through specialist certification acquisition Year 3: 500,000-1,000,000 yen increase through advanced certification acquisition, etc.
Steady income increases can be achieved through continuous skill development.
Freelance Income Potential
Going independent as a freelancer can lead to higher income opportunities.
Rate settings vary by experience and skill level. Looking at infrastructure engineer freelance job postings and project rates, the average monthly rate is around 700,000 yen, with top rates reaching 2 million yen per month.
Success as a freelancer requires not only technical expertise but also project management ability and communication skills.
Securing stable projects, appropriate insurance coverage, and knowledge of tax and accounting are also important.
Keys to Stable Income as a Freelance Infrastructure Engineer
Annual income is calculated based on project rates and working days, so appropriate project selection and utilization rate management are crucial.
Benefits and insurance become self-responsibility, requiring financial planning that accounts for these costs.
Reference: Freelance Start
6.Future Prospects and Income Outlook for Infrastructure Engineers

Demand for infrastructure engineers is expected to further increase with the acceleration of digital transformation (DX).
Below, we’ll detail future prospects and associated income possibilities.
Demand Forecast for Infrastructure Engineers in Japan
In the future IT talent market, three areas are particularly expected to grow “cloud infrastructure” “security” and “automation/efficiency”
In cloud infrastructure, demand is increasing for hybrid cloud environment construction, multi-cloud management, and cloud-native technology.
In security, demand is growing for specialists in zero-trust architecture, cloud security, and control system security.
In automation and efficiency, demand is expanding for engineers skilled in Infrastructure as Code, AI operations automation (AIOps), and serverless architecture.
Future Salary Levels and Prospects
Projected salary levels over the next five years vary significantly by specialization.
Infrastructure engineers with specializations in cloud or security can particularly expect salary increases.
Even as job content and required technologies change, the fundamental demand for infrastructure engineers is expected to persist.
Investment and Returns Needed for Career Advancement
Achieving high future income requires planned investment. Education and certification costs include cloud certifications, security certifications, and technical training.
Exam fees range from under 10,000 yen to over 50,000 yen, plus additional costs for certification study materials.
Time investment includes 10-15 hours weekly for self-study, 3-6 months study period for certifications, and about 20 hours monthly for technical training.
Returns on certification investments include salary increases, improved market value, and expanded career options.
Long-term benefits include further income increases, established market value through specialization, and management career opportunities.
Sustained Demand for Infrastructure Engineers
Infrastructure engineers have strong future prospects, particularly in cutting-edge fields like cloud and security, where continued demand growth is expected.
However, rapid technological evolution requires regular skill updates and investment in new technologies. Maintaining market value through planned learning and practice is essential.
7.Rising Market Value of Japanese Infrastructure Engineers
Infrastructure engineer market value is expected to further increase with accelerating digitalization. Particularly in cloud and security fields, developing expertise can lead to substantial income increases.
Achieve steady salary increases through planned skill development and strategic career choices.