What is the salary level for software engineers in Japan? With various factors affecting compensation levels, including years of experience, skills, company size, and work location, what kind of career development is required to increase annual income?
This article provides comprehensive information about salaries, from current market trends to future prospects.
- Japanese software engineer salaries range from 3M to 8M yen based on experience level
- Foreign companies offer up to 20M+ yen while Japanese companies cap at around 8M yen
- Remote work is reducing regional pay gaps and driving performance-based compensation
1. Current State of Software Engineer Salaries in Japan
In recent years, with the acceleration of digital transformation (DX) and growth in the technology industry, the demand for software engineers has been steadily increasing.
This increased demand is reflected in salary levels, with an upward trend continuing across the industry. Let’s examine each aspect in detail.
Industry-wide Average Annual Income and Salary Ranges
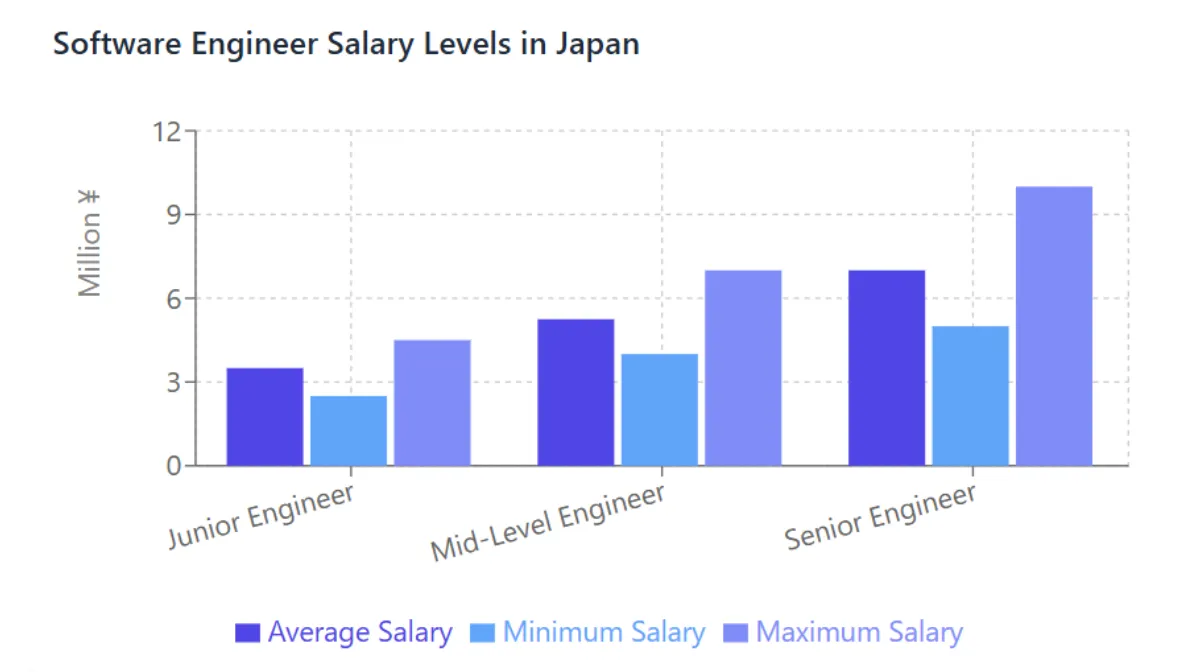
Software engineer salaries in Japan vary significantly based on skill level and experience.
| Engineer Level | Years of Experience | Average Annual Salary | Salary Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Junior Engineer | New Graduate | ¥3-4 million | ¥2.5-4.5 million |
| Mid-Level Engineer | 3-5 years | ¥4.5-6 million | ¥4-7 million |
| Senior Engineer | 5-10 years | ¥6-8 million | ¥5-10+ million |
The industry-wide average annual income is approximately 4.8 million yen, but this figure varies significantly depending on company size, region, and specialization.
Particularly in cutting-edge technology fields such as cloud computing, AI, and security, salary levels significantly higher than average are common.
Salary Comparison by Company Size
Company size is one of the major factors affecting salary levels.
- Large Companies (1000+ employees)
Base salaries are set relatively high, with bonuses typically paid twice a year, equivalent to 4-6 months of salary. Benefits are comprehensive, and annual income ranges from 4 to 12 million yen. - Mid-sized Companies (100-999 employees)
Base salaries are around industry average, with bonuses paid twice yearly, equivalent to 3-4 months of salary. Annual income ranges from 3.5 to 8 million yen. - Startup Companies (fewer than 100 employees)
Base salaries are variable with a higher proportion of performance-linked compensation. Stock options are often granted, and annual income ranges widely from 3 to 12+ million yen.
Salary Changes Based on Years of Experience
Software engineer salaries tend to increase incrementally with years of experience. The first three years after graduation are considered a period for acquiring basic development skills, with average annual increases of 5-10%.
Years 4-7 become a period for establishing specialization, with average annual increases of 10-15%. This is also an important time for gaining management skills through leadership experience.
After 8 years, engineers enter a period of demonstrating advanced specialization, with variable annual increase rates of 5-20%. This period marks an important crossroads for choosing between management and specialist career paths.
2. Factors Affecting Software Engineer Salaries

Software engineer salaries are determined by various factors. Understanding these factors and strategically building one’s career can lead to higher compensation.
Impact of Skills and Technology Stack
One of the major factors that significantly affects an engineer’s salary is their skill set and technology stack. For example, having experience with high-demand technologies in the following areas directly impacts salary levels:
Cloud technology experience with AWS, Azure, GCP, cloud architecture design capabilities, and microservice implementation experience are valued.
In the AI/machine learning field, experience with frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, practical data science experience, and MLOps knowledge are sought after.
In the security field, security design and implementation experience, vulnerability assessment and countermeasure capabilities, and various security certifications are evaluated.
Possessing technical skills can lead to a 10-30% increase in base salary. Strategic acquisition of high-market-value skills is an important element for salary increases.
Differences by Position and Role
Positions and roles within an organization significantly impact salary levels. These include technical leaders who are responsible for project-wide technical strategy planning and team member development, architect positions who have decision-making authority in system design and technology selection, and engineering managers who are responsible for team management, talent development, and evaluation.
Geographic Salary Differences
Location also significantly impacts salary levels. The Tokyo metropolitan area has the highest salary levels, and using Tokyo central areas as a baseline, other major cities like Osaka and Nagoya maintain levels at 85-95% of Tokyo rates. Regional cities typically offer 70-85% of Tokyo rates, though living costs are lower.
Remote Work Reducing Regional Gaps
With the recent proliferation of remote work, regional salary gaps are gradually narrowing. Opportunities to work at urban salary levels while living in regional areas have increased, as have recruitment opportunities from overseas companies.
There is a growing trend toward merit-based compensation rather than location-based differences, enabling flexible work arrangements unrestricted by location.
3. Career Paths to Achieve High Compensation

To achieve high compensation as a software engineer, it’s important to chart clear career paths and systematically accumulate skills and experience.
Career Development as a Specialist
To achieve high compensation as a technical specialist, establishing outstanding expertise in specific technical fields is required. Engineers should select high-market-value technical areas and aim for early entry into promising technologies while deepening specialization and acquiring knowledge of related technologies.
For building track records, it’s effective to make technical capabilities visible through contributions to open-source projects, writing technical blogs, and speaking at technical conferences. Additionally, aiming for promotion to tech lead or architect positions and establishing oneself as an industry expert can lead to higher income.
Specialist annual income ranges from 6 to 15 million yen, depending on experience and achievements.
Income Increase Through Management Position Transition
Another effective career path is to acquire management skills while maintaining technical capabilities as a foundation to aim for higher income.
Starting with team leader experience, engineers gain project management skills and practical experience in member development. At the middle level, they handle management of multiple teams, budget and human resource planning, and department strategy formulation. At the senior level, they oversee entire development departments, bridge with management, and formulate technical strategies.
Management position annual income ranges from 8 to 20 million yen, depending on position and company size.
Income Increase Strategy Through Freelance Work and Side Jobs
It’s also possible to aim for more flexible income increases through freelance work or side jobs rather than traditional employment forms.
As freelancers, engineers can select projects utilizing their expertise, handle multiple projects simultaneously, and increase rates through direct contracts. For side jobs, they can select projects compatible with their main job, such as technical advisory roles, consulting, and utilizing online platforms.
Additionally, diversifying revenue through technical education and training businesses, content sales, and development and operation of original products can be effective.
Freelance total income typically ranges from 8 to 20 million yen, with side job income expectations of 2 to 5 million yen.
4.Salary Comparison Between Foreign and Japanese Companies
In the Japanese software engineer market, there are significant differences in salary systems and levels between foreign and Japanese companies. Understanding these characteristics is important for career choice decisions.
Foreign Companies’ Salary Systems and Characteristics
Foreign companies’ salary systems tend to be more performance-based following global standards and generally offer higher compensation levels.
Base salaries are set higher based on market value, with job-based pay systems allowing flexible salary settings based on experience and skills. Incentive systems are also comprehensive, including performance-linked bonuses, stock options, and sign-on bonuses.
For promotion and advancement, there are many opportunities for merit-based early promotion and global mobility. For engineers with 5+ years of experience, annual income ranges from 6 to 20+ million yen.
Japanese Companies’ Salary Systems and Characteristics
Japanese companies’ salary systems retain elements of seniority-based progression while increasingly incorporating performance-based elements.
Base salaries include seniority elements, with many companies using a mix of skill-based and role-based pay. Gradual salary increases based on years of service are also characteristic.
Bonuses are typically paid regularly in summer and winter, with various allowances well-established. Reliable payment of overtime allowances is also characteristic of Japanese companies.
Welfare benefits include comprehensive social insurance, housing allowances, family allowances, and retirement benefit systems. For engineers with 5+ years of experience, annual income ranges from 4.5 to 8 million yen.
Japanese Salary Levels in the Global Market
Compared to the global market, Japanese software engineer salary levels are not particularly high. Due to smaller differences from other occupations, satisfaction with compensation tends to be low.
The United States, in particular, has an average annual income of over 11 million yen, nearly double that of Japan. While India’s average annual income is slightly lower at about 5 million yen, it represents nearly nine times the national average across all industries, resulting in very high satisfaction levels and salary standards for software engineers as a profession.
However, salary levels are trending upward due to increased DX demand, intensified global competition, and serious talent shortages. With the spread of remote work, salary standardization is also progressing. Going forward, convergence toward global standards is expected to strengthen, and performance-based evaluation is likely to become more common.
■日本でエンジニアとしてキャリアアップしたい方へ
海外エンジニア転職支援サービス『 Bloomtech Career 』にご相談ください。「英語OK」「ビザサポートあり」「高年収企業」など、外国人エンジニア向けの求人を多数掲載。専任のキャリアアドバイザーが、あなたのスキル・希望に合った最適な日本企業をご紹介します。
▼簡単・無料!30秒で登録完了!まずはお気軽にご連絡ください!
Bloomtech Careerに無料相談してみる
5.Keys to Successful Salary Negotiation

Salary negotiation is one of the important skills in an engineer’s career. With proper preparation and strategic approach, it’s possible to obtain compensation that matches one’s market value.
Preparation and Achievement Building to Increase Market Value
The foundation for successful salary negotiation is increasing one’s market value and creating achievements that can be objectively demonstrated. It’s important to systematically organize achievements and prepare to present them effectively during negotiations.
Writing and publishing technical articles, contributing to open source, and speaking at technical conferences are effective ways to demonstrate technical capabilities. Building portfolios, quantifying project results, collecting customer evaluations and feedback are important for making achievements visible. Market research on industry trends and competitor salary levels is also crucial.
Regarding achievements, quantitative results can demonstrate specific cost reductions, productivity improvements, and sales contributions. Qualitative evaluations include important elements such as team contributions, technical influence, and leadership demonstration.
Salary Negotiation During Job Changes
Salary negotiation during job changes is an important opportunity to achieve significant income increases.
In preparation, it’s important to organize current total compensation in detail, clarify desired conditions, and set ranges for possible concessions. The negotiation process begins with initial condition presentation, and having multiple alternatives prepared enables flexible responses.
Proposing additional value beyond salary can also be effective. When presenting market value, showing specific figures like “the market rate for similar positions is XX yen” is effective. In explaining value, demonstrating specific contributions and achievements, and making constructive proposals such as gradual salary increase plans can be useful.
Measures to Achieve Desired Raises and Promotions
To achieve raises and promotions in current positions, steady achievement building during evaluation periods is important. It’s necessary to exceed expected results, launch new projects, and clearly demonstrate contributions to the team.
In building relationships with supervisors, regular one-on-ones are used to share career plans and make achievements visible. For promotions and raises, accurately understanding required skills, expected roles, and evaluation criteria is important.
Based on this understanding, systematically progress through resolving skill gaps, gaining leadership experience, and participating in cross-departmental activities. When proposing promotions, it’s effective to demonstrate future vision, explain team contributions, and present specific action plans.
6. Future Prospects and Salary Outlook for Japanese Software Engineers

The Japanese software engineer salary market is entering a major transformation period due to rapid technological evolution and work style reform promotion.
Technology Trends and Job Market Changes
With the emergence of new technologies, the skill sets required of engineers and accompanying salary levels are changing significantly.
In the AI/machine learning field, demand for specialized engineers is rapidly increasing, with average salaries trending 20-40% higher. In cloud-native development, the importance of multi-cloud compatibility is increasing, enhancing the value of DevOps engineers. In Web3.0-related technologies, there are increasing opportunities for high compensation for blockchain developers and roles in emerging companies.
Recruitment forms are also diversifying, with job-based employment becoming more common, side jobs and multiple employment normalizing, and the freelance market expanding. Required personnel profiles are changing, with increasing importance placed on multi-domain skill possession, business understanding, and global communication abilities.
Remote Work’s Impact on Software Engineer Salaries
With the spread of remote work, geographic constraints are being eliminated, increasing opportunities for regional residents to participate in urban projects. Direct employment from global companies is also increasing, and regional salary gaps are narrowing.
Work styles are diversifying, making it easier to work for multiple companies simultaneously and adopt reduced or flexible hours, with performance-based employment forms increasing.
Evaluation systems are also changing, with clearer performance criteria, establishment of remote environment evaluation methods, and visualization of team contributions. Building relationships online, asynchronous communication, and addressing cultural differences are also becoming important challenges.
Future Salary Trend Predictions
In the short term, IT talent shortages are expected to continue, with convergence toward global standards and widening gaps based on specialization. Compensation systems are changing, with increases in performance-linked systems, flexible salary design, and normalization of stock compensation.
In the medium to long term, standardization of global salary levels, work transformation through AI utilization, and creation of new job types are expected. Career paths are diversifying, with increasing opportunities for combining expertise with management, cross-border activities, and independent entrepreneurship.
Adapting to Changes for Salary and Career Growth
To adapt to various changes, early entry into cutting-edge technologies, strengthening business skills, and improving global adaptability are important. Establishing continuous learning habits, updating portfolios, and building networks are also necessary elements for maintaining market value.
7.Japanese Software Engineer Salary Market at a Turning Point
The software engineer salary market is entering a major turning point due to changes in technology trends and work style reforms.
As the transition progresses from traditional seniority-based salary systems to more global and performance-based systems, individual engineers’ market value is becoming more important than ever.
Continuous skill improvement and strategic career building to enhance one’s market value will be key to salary increases in the coming era.
▼Related Reading | Salary Situations for Various Engineers
For foreign engineers who are considering working in Japan, we introduce content that summarizes salary situations for various types of engineers.
We cover AI engineers, infrastructure engineers, data engineers, DevOps, and others, so we hope this will be a useful reference for you.